
May 22, 2022
Protecting Species, Forests, and the Climate
- as seen by -
 Sarah Markes
Sarah Markes
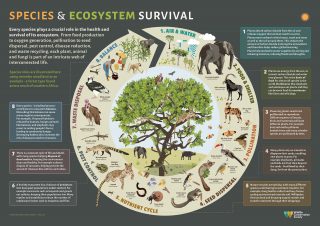
Chimpanzees – our closest relatives are now classified as Endangered by the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Surviving in a variety of primary and secondary forest habitats across Africa, there are believed to be only around 405,000 individuals left in the world. Chimpanzee populations are decreasing across the continent due to habitat loss, disease, and hunting, yet like millions of other species, they play a crucial role in the ecosystems that sustain us.
As many of us are now aware, forests are home to a wealth of flora and fauna and provide crucial ecosystem services such as water catchment, rainfall regulation, flood mitigation, and soil conservation for communities that live in and around them. Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere which they store in their leaves, branches, and forest soils. Tropical forests store a very high level of carbon compared to other habitats and land uses thus protecting them is hugely important in climate change mitigation efforts to safeguard people the world over. So, humans, chimpanzees, and millions of other species are reliant on forests for their well-being and survival.
This is not a one-way process, however. Chimpanzees, like many other primates, disperse seeds from the fruit they eat and fertilize them with their dung. This helps new trees grow and replace the old. Seed dispersal is also becoming increasingly important as climate change affects temperature and weather patterns. Some tree species may only be able to survive cooler temperatures at higher altitudes for example, so the more seeds that primates and birds transport to higher ground, the more are likely to survive.
Sourcing support and funds for conservation is an eternal challenge, and so-called flagship species such as chimpanzees can help raise awareness of the importance of protecting areas that may otherwise be neglected. These charismatic species can also be the basis of ecotourism activities that support conservation.
Tanzania is home to Africa’s southern-most wild chimpanzee population – comprising a subspecies known as the eastern chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes ssp. Schweinfurthii). In recent years, this southern Tanganyika population has declined due to deforestation and hunting, so the Wildlife Conservation Society is working with government and communities to help address this. Education and awareness-raising are part of this work, and this poster was created to support this. Print resolution files are available from sarahindar@gmail.com.
EDITOR’S NOTE: This post celebrates Biodiversity Day 2022, which has the theme “Building a shared future for all life.”



Comments